Why use a password generator?
Digital security is one of the most important issues, especially in times when hacker attacks, data leaks and identity theft have become so common.
For this reason, protecting your information online has never been more important. Passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access, whether to email accounts, systems or social networks. There are many cases of people having their social media accounts hacked by malicious groups.
Many users underestimate the importance of passwords in protecting their online environments, using weak, easily identifiable combinations (such as birth dates), simple sequences (abcde, 123456) or repeating the same password on multiple services.

Having secure and diverse passwords can therefore be a challenge for creativity. That's why we've provided this secure password generator.
But what are secure passwords, how can you increase your level of protection and which services can help you in your day-to-day life?
Want to know what else is important? Protecting your email marketing from invalid emails, temporary emails and spamtraps. Create a SafetyMails account now and check your emails.
On this page, you will see:
- What makes a password strong.
- How to identify password leaks.
- Tools and practices to improve your digital security.
The value of strong passwords
In July 2024, a hacker released a file named “RockYou2024” containing almost 10 billion leaked passwords (BitDefender).
Passwords are the main key to protecting your data from unauthorized access on digital platforms. Without them, anyone could read the contents of your emails, gain access to sensitive documents, bank accounts, conversations on direct messaging apps, make posts on social networks, and so on.
In other words, passwords are the first layer of protection for your digital life. And that's why this topic needs to be given due attention and importance. Digital criminals are trying to crack passwords and gain access to apply their scams, through brute force attacks, phishing and social engineering.
That's why this first layer of protection, the password, must always be strong. But what is a strong password and what makes a password strong?
Strong password: what is it and how to do it?
A strong password is one that cannot be easily guessed or cracked. Therefore, a strong password is one made up of a sequence of characters capable of frustrating attempts to break it.
For a password to be considered strong, it is important to consider some fundamental aspects:
- Length: at least 16 characters. The more characters, the better.
- Variety: include uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers and symbols.
- Randomness: don't follow any logical sequence, such as well-known words or numbers.
- No personal information: avoid names or well-known dates, such as birthdays.
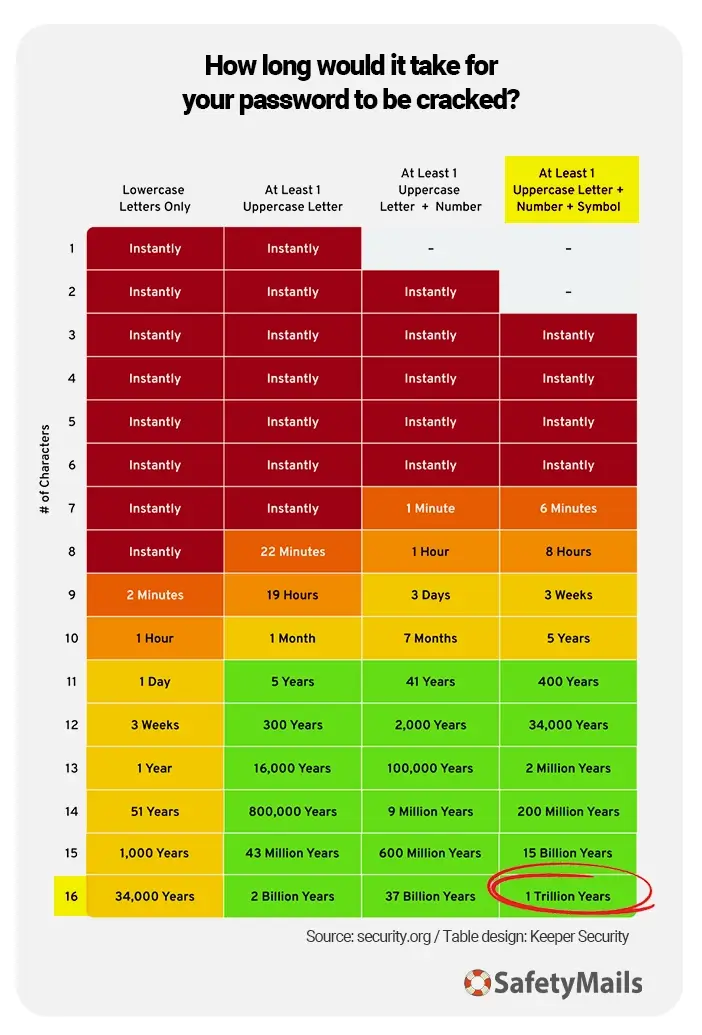
For this reason, passwords such as “123change”, “johnny123” and “123456” are considered weak and are not recommended. The company NordPass has a list of common and easily guessed passwords. Just to give you an idea, passwords like “12346” only take 1 second to crack and have been identified in accesses more than 3 million times.
On the other hand, according to Security.org, a password that follows the recommendations given for length, diversity and randomness could take 1 trillion years to crack.
A good example of a secure password would be “f9#ixLKk$fPX@0Rq”. Want a password like that? Take advantage of SafetyMails' strong password generator.
You can also get a creative email name with SafetyMails. Create your new email account and protect it with our secure password suggestion!
Of course, strong passwords are the best, but they are also the most complicated to remember. Having different passwords for all your accesses then makes the task impossible.
That's why having a password manager makes all the difference.
Password managers
With so many passwords to create and manage, relying on memory can be risky. This is where password managers can be extremely useful. Managers store and encrypt (very importantly) your passwords, freeing you from the need to memorize them.
We'll help you choose some free and paid password managers. Some of them offer support for desktops (Windows, macOS, Linux), smartphones (iOS, Android) and web browser extensions.
10 suggestions of popular password managers:
1. KeePass (Free)
- Description: Open source password manager, ideal for advanced users who prefer to store passwords locally. It must be installed and has no online access.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Linux (with browser extensions).
- Pricing: free.
- Website: keepass.info
2. LastPass ($)
- Description: one of the best-known password managers, offers secure password storage, autofill and password generation.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: free (limited) or premium from US$ 3.00 per month or US$ 18.00 per year.
- Website: lastpass.com
2. RoboForm ($)
- Description: offers ease of use and excellent cost-effectiveness for individual users and families.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: free or premium from US$ 18.00 per year.
- Website: www.roboform.com
2. NordPass ($$)
- Description: created by the developers of NordVPN, focuses on security and simplicity.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: free (limited) or premium from US$ 21.48 per year.
- Website: nordpass.com
4. Zoho Vault ($$)
- Description: offers solutions for both individuals and companies. Focused on team management.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS.
- Pricing: free plan or premium from US$72.00 per year.
- Website: www.zoho.com/vault/
5. Enpass ($$)
- Description: allows local storage or synchronization with cloud services.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS.
- Pricing: paid from US$24.00 per year or US$99.99 (lifetime).
- Website: www.enpass.io
6. 1Password ($$$)
- Description: offers solutions for both individuals and companies, focusing on simplicity. It offers safes for different types of information.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: paid from €31.80 per year.
- Website: 1password.com
7. Keeper Security ($$$)
- Description: manager with advanced features for corporate and personal protection, including dark web monitoring.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: paid from US$34.99 per year.
- Website: keepersecurity.com
8. Bitwarden ($$$$)
- Description: open source platform, praised for its transparency and security. It has a very complete free plan.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: free plan or premium from US$ 48.00 per year.
- Website: bitwarden.com
9. Dashlane ($$$$$)
- Description: combines a password manager with additional features such as dark web monitoring and integrated VPN in the premium plan.
- Platforms: Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, browser extensions.
- Pricing: free (limited) or premium from US$240.00 per year.
- Website dashlane.com
Double factor authentication (2FA): a powerful ally
Two-factor authentication (2FA), also known as two-factor authentication, is a security method that requires two different forms of verification to allow access to an account or system. That way, even if your password is cracked, you will still need to go through this second authentication step, adding an extra layer of protection against unwanted access.
Normally, access is authenticated using one of the following three methods:
- Using data you know: a password, PIN or access code.
- Using something you own: a physical device such as a cell phone, security card, hardware token, etc.
- Recognizing something you are: fingerprint, facial recognition, voice, etc.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) usually uses two of these factors to reinforce the security of the login.
So, for example, after entering your password (something you know), you may receive a one-time code on your cell phone (something you have), which needs to be entered to complete the login.
Some types of two-factor
Here are some of the most common types of two-factor authentication:
- SMS or Email: the most common means, where the user receives a code (by email or SMS) which must be entered to authenticate access. It is easy to use and does not require the installation of applications, but it is vulnerable to message interception and SIM swap attacks.
- Authenticator apps: these are apps such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator or Authy, which generate one-time temporary codes.
- Hardware tokens: these are physical devices, such as smart cards or USB devices, which need to be connected for authentication.
- Biometrics: uses the owner's physical characteristics, such as fingerprint, facial, voice or iris recognition, for authentication.
- Push notifications: an alert is sent to a mobile device, allowing the owner to recognize and approve access or deny it with one touch.
- Time-based tokens: generate temporary codes on a device, such as authenticator apps or hardware tokens, widely used by banks.
Regarding 2FA authentication applications, we've put together four suggestions for you to install:
- Google Authenticator: simple to use, generates time-limited verification codes and is compatible with a wide range of online services.
- Microsoft Authenticator: excellent for users who use Microsoft services, but also compatible with other online services. In addition to verification codes, it offers passwordless authentication for more secure logins.
- Authy: this app offers extra features, such as cloud backup for easy recovery in the event of loss or replacement of devices. It has a user-friendly interface.
- Duo Mobile: offers a wide range of authentication features, including push notifications, verification codes and support for multiple accounts.
To install, simply go to your app store (Google Play, Apple Store), search for the app you're interested in and install it.
All of these applications are free, easy to use and offer an extra layer of security for your online accounts. Choosing the right one may depend on personal preferences, devices used and integration with the services you use.
Using biometrics as a protection element
The use of biometrics, such as fingerprints, offers convenience and security, but also requires some precautions to ensure that your data is properly protected.
As previously mentioned, biometrics is the use of the owner's physical characteristics. Of the methods available, fingerprinting is the most common type of biometrics. Although it is very secure from an access point of view, as it is difficult to replicate (because the person has unique patterns), it requires a higher level of care from the user, as it is information that cannot be altered.
Another drawback of biometrics: if a registered fingerprint is compromised by, say, a small cut on the finger, it can already cause difficulties when using it.
Below are important recommendations for using fingerprints as an authentication method:
- Avoid setting up biometrics in non-secure environments: for example, when accessing buildings where you don't go often.
- Prefer devices that store biometric data locally and not on cloud servers.
- Disable its use in specific cases: depending on the application, you can temporarily disable biometrics and give preference to PINs or patterns.
How to know if your passwords have been compromised
Staying informed and proactive is essential to ensure the security of your personal information in the digital environment.
In January 2024 there was what became known as the “Mother of All Leaks” (MOAB), with a total of 26 billion password records, totaling 12 terabytes of information (McAfee).
A password leak or breach can compromise your digital security.
So keep an eye out for signs, such as receiving password confirmation emails that you didn't request.
Suggested leak information services
To make everyday life easier, there are online services that allow you to check whether your passwords have been exposed in data leaks.
Be careful when choosing a service! Make sure it complies with privacy and data protection laws. Never enter your login and password together. If you are looking to find out if your email or login has been leaked, do not enter your password. If you are looking to find out if your password has been leaked, never enter your login or e-mail address.
When accessing these services, if you identify that your data has been exposed, change the compromised passwords immediately and remember to always have two-factor authentication enabled.
Here are some services where you can find out if your password has been leaked:
1. Have I Been Pwned
- Description: one of the best-known sites for checking whether your email or password has been compromised in data leaks. It maintains an up-to-date database with billions of records.
- How it works: you enter your e-mail or password, and the site checks to see if it has appeared in any known leaks.
- Website: https://haveibeenpwned.com
2. Firefox Monitor
- Description: Firefox browser tool, integrated with the Have I Been Pwned database, which allows you to monitor your personal data in leaks.
- How it works: you enter your e-mail address, and the site notifies you if it has been compromised. It also offers alerts for new leaks.
- Website: https://monitor.firefox.com
3. DeHashed
- Description: a search engine for leaked data, including passwords, usernames, phone numbers and more. It is used by both users and security professionals.
- How it works: enter your information to check if it has been exposed. Offers free and paid plans.
- Website: https://dehashed.com
4. LeakCheck
- Description: a tool for checking data leaks, with a focus on passwords. In addition to email, it allows you to search for usernames and even specific passwords (never type login and password together).
- How it works: you enter the information to check your exposure in leaked databases.
- Website: https://leakcheck.io
5. CyberNews Personal Data Leak Checker
- Description: CyberNews' free service that allows you to check if your e-mail has been exposed in known leaks.
- How it works: enter your e-mail address and receive a report with the associated leaks.
- Website: https://cybernews.com/personal-data-leak-check
6. SpyCloud
- Description: a tool aimed at companies, but which also allows users to check whether their credentials have been compromised.
- How it works: enter your e-mail address to check for leaks in a vast database.
- Website: https://spycloud.com
7. Kaspersky Password Check
- Description: a tool offered by Kaspersky that evaluates the strength of your passwords and checks whether they have been compromised in known leaks.
- How it works: you enter your password, and the tool analyzes its strength and presence in databases of leaked passwords.
- Website: https://password.kaspersky.com
Implications of password leaks
In the case of password leaks, you can face serious consequences, such as:
- Identity theft: cybercriminals can impersonate you by stealing your identity. For example, think of the complications involved in cases where access to Instagram has been stolen and criminals make false promises or controversial posts posing as the account owner.
- Financial damage: accessing bank accounts or demanding ransoms for stolen social networks are some examples of the financial damage that broken passwords can bring.
- Damage to reputation: during identity theft from email and social networks, texts and posts can be made with various contents (sexual, prejudiced, etc.) that cause damage to the reputation of the real owner of the account. The effort and time needed to undo this damage can be immense.
What can you do to prevent leaks?
The best security mechanism is prevention. Therefore, acting proactively is very important to prevent passwords from being cracked or stolen.
These are some of the main reasons why passwords are exposed:
- Weak and reused passwords: simple and repeated passwords on multiple accounts facilitate brute force attacks and other intrusion techniques. Have different passwords for different accesses.
- Phishing attacks: actions by cybercriminals who trick users into revealing their passwords on fake websites or via malicious emails.
- Malware and Keyloggers: programs installed on your device that can capture passwords you type or store in unprotected files.
- Human error and negligence: sharing passwords in chats, writing them down on paper, among others, are common mistakes that expose passwords.
- Unauthorized access by insiders: employees or co-workers with bad intentions can use their privileged access to systems to steal passwords. The 'Cost of Insider Threats Global Report' (Ponemon Institute 2023) revealed that 55% of security incidents involved negligent or malicious insiders.
Tips for keeping your passwords safe
So, to keep your passwords safe, you can do the following:
- Never write down your passwords on paper or in unprotected files on your computer.
- Use password managers to organize and protect your information.
- Enable two-factor authentication and login notifications when your accounts are accessed.
- Don't click on hyperlinks in suspicious emails.
- Limit employee access to sensitive data and maintain alert mechanisms in the event of suspicious use.
Conclusion
Password security is the basis for digital protection. By combining good practices, reliable tools and technologies such as 2FA, you can significantly reduce online risks.
To simplify your routine and increase your security, try SafetyMails' automatic secure password generator. It's a practical and efficient solution that helps you keep your information safe.
Don't put off your security until later. Create strong passwords now and protect your accounts!